Day 20 - Take an interest and join a faction!
Learning Targets:
Students will be able to explain why and how...
- Explain the benefits and potential problems of interest-group influence on elections and policy making.
- Interest groups may represent very specific or more general interests, and can educate voters and office holders, draft legislation, and mobilize membership to apply pressure on and work with legislators and government agencies.
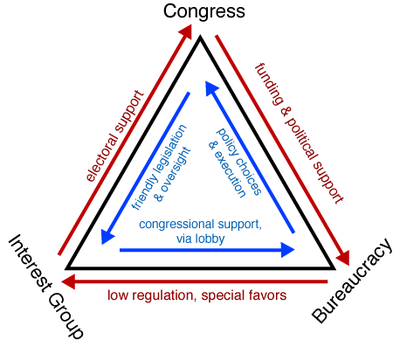
- In addition to working within party coalitions, interest groups exert influence through long-standing relationships with bureaucratic agencies, congressional committees, and other interest groups; such relationships are described as “iron triangles” and issue networks and they help interest groups exert influence across political party coalitions.
Opener: Interest Group Inventory
What do you want to be when you grow up? Chances are, there is an interest group that represents that profession.
Task: Find at least 2 professional organizations/interest groups that are associated with the job or career field that you are planning on joining after you finish school. Additionally, find at least one interest group that you might be interested in that is NOT tied to a profession or industry, but rather a social or political issue.
Activity #1: - Interest Groups and PACs
Working alone, or with a partner, answer the following questions in your notebook.
1. Which interest groups would you argue have the most influence in Congress?
2. Which groups spend the most money on campaigns/PACs?
3. How do the interest groups that you found in the class opener compare to the groups you listed in questions 1 and 2?
Activity #2: Interest Groups - N-50
LD - an organization of people who share a common interest and mobilize to protect and promote that interest by influencing both elected and bureaucratic members of the government.
SD -
Examples - NRA, AARP, MADD, https://www.opensecrets.org/industries/mems.php
Non-Examples - Bureaucracy (CDC, FDA, FEC, etc), Political Parties
Related Terms - PAC's (Political Action Committees), Lobbyist, Voting Behavior, Incumbents
Close - Exit Ticket - ASAP+
AMONG the numerous advantages promised by a well-constructed Union, none deserves to be more accurately developed than its tendency to break and control the violence of faction. By a faction, I understand a number of citizens, whether amounting to a majority or a minority of the whole, who are united and actuated by some common impulse of passion, or of interest, adversed to the rights of other citizens, or to the permanent and aggregate interests of the community.
- James Madison, 1788, Federalist #10
Faction=Interest Group?
Learning Targets:
Students will be able to explain why and how...
- Explain the benefits and potential problems of interest-group influence on elections and policy making.
- Interest groups may represent very specific or more general interests, and can educate voters and office holders, draft legislation, and mobilize membership to apply pressure on and work with legislators and government agencies.
- In addition to working within party coalitions, interest groups exert influence through long-standing relationships with bureaucratic agencies, congressional committees, and other interest groups; such relationships are described as “iron triangles” and issue networks and they help interest groups exert influence across political party coalitions.

Opener: Interest Group Inventory
What do you want to be when you grow up? Chances are, there is an interest group that represents that profession.
Task: Find at least 2 professional organizations/interest groups that are associated with the job or career field that you are planning on joining after you finish school. Additionally, find at least one interest group that you might be interested in that is NOT tied to a profession or industry, but rather a social or political issue.
Activity #1: - Interest Groups and PACs
Working alone, or with a partner, answer the following questions in your notebook.
1. Which interest groups would you argue have the most influence in Congress?
2. Which groups spend the most money on campaigns/PACs?
3. How do the interest groups that you found in the class opener compare to the groups you listed in questions 1 and 2?
Activity #2: Interest Groups - N-50
LD - an organization of people who share a common interest and mobilize to protect and promote that interest by influencing both elected and bureaucratic members of the government.
SD -
Examples - NRA, AARP, MADD, https://www.opensecrets.org/industries/mems.php
Non-Examples - Bureaucracy (CDC, FDA, FEC, etc), Political Parties
Related Terms - PAC's (Political Action Committees), Lobbyist, Voting Behavior, Incumbents
Close - Exit Ticket - ASAP+
AMONG the numerous advantages promised by a well-constructed Union, none deserves to be more accurately developed than its tendency to break and control the violence of faction. By a faction, I understand a number of citizens, whether amounting to a majority or a minority of the whole, who are united and actuated by some common impulse of passion, or of interest, adversed to the rights of other citizens, or to the permanent and aggregate interests of the community.
- James Madison, 1788, Federalist #10
Faction=Interest Group?





No comments:
Post a Comment